Influence of School Climate and Work Motivation of Teacher on Work Effectiveness of Teacher in the Digital Age under the Secondary Educational Service Area Office Bangkok 2
Main Article Content
Abstract
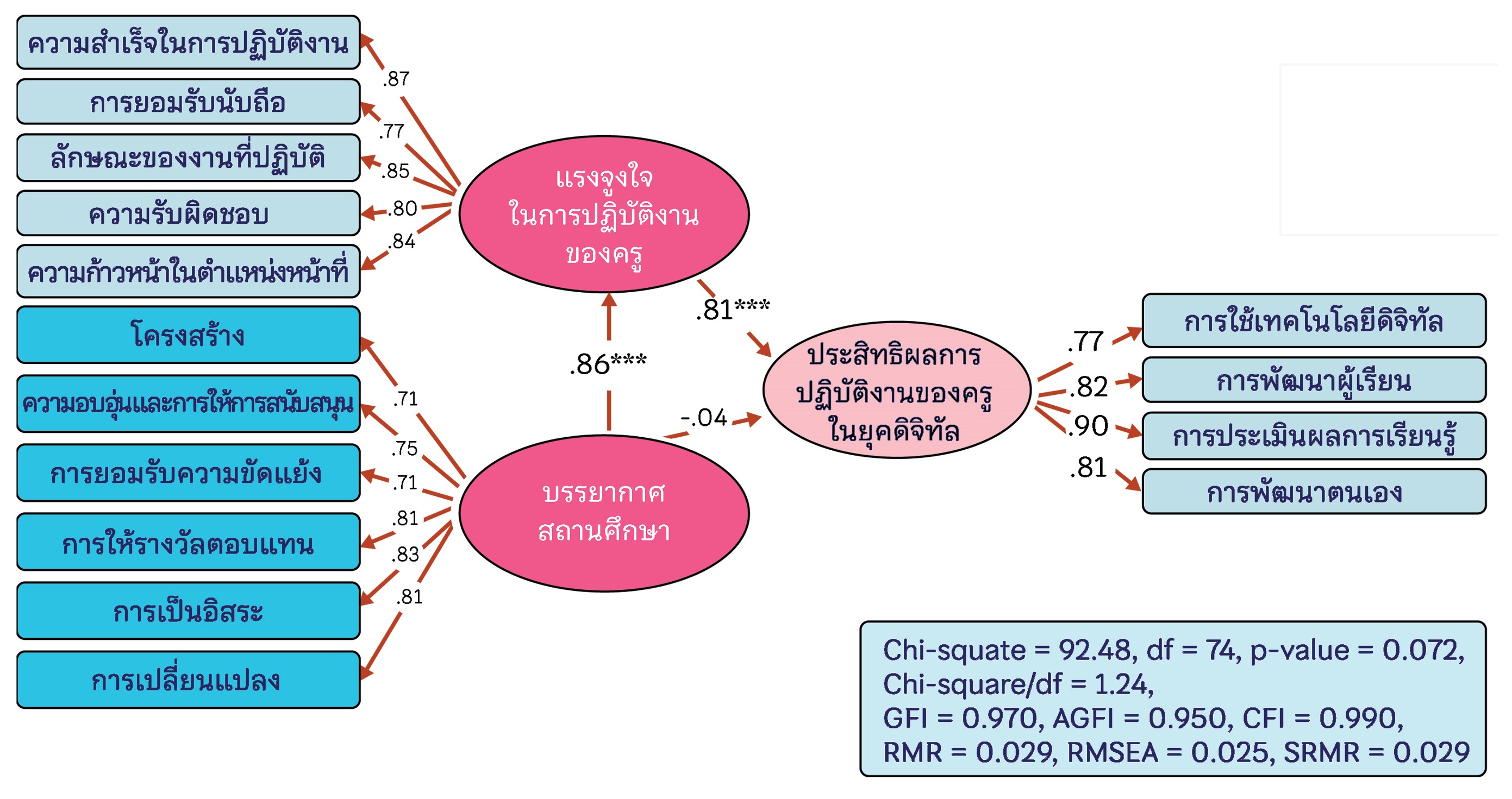
The purposes of this research were the direct and indirect influences study the direct and indirect influences on the performance effectiveness of teachers in the digital era. The sample used in this study consisted of 361 teachers under the Secondary Educational Service Area Office Bangkok 2, determined by the Krejcie and Morgan table. The questionnaire used a 5-level rating scale with a reliability of 0.968. The statistics used for data analysis were linear structural equation modeling (SEM) to examine the consistency between the research model and the empirical data.
The research results found that: The model was consistent with the empirical data, considering the statistical values: Chi-square = 92.48, df = 90, p-value = 0.072, GFI = 0.970, AGFI = 0.950, SRMR = 0.029, RMSEA = 0.025. The variables in the model could explain 60 percent of the variance in the performance effectiveness of teachers in the digital era (R2 = 0.6). The variable with a direct influence on the performance effectiveness of teachers in the digital era was the teachers' work motivation variable, statistically significant at a level of .001. When the teachers' work motivation variable increased, the performance effectiveness of teachers in the digital era variable also increased. Moreover, the school climate variable had an indirect influence on the performance effectiveness of teachers in the digital era variable, statistically significant at a level of .001, with the teachers' work motivation variable as the mediating variable. This indicates that when the school climate variable increased, it would affect the teachers' work motivation variable, leading to an increase in the performance effectiveness.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
เพื่อให้เป็นไปตามกฎหมายลิขสิทธิ์ ผู้นิพนธ์ทุกท่านต้องลงลายมือชื่อในแบบฟอร์มใบมอบลิขสิทธิ์บทความ ให้แก่วารสารฯ พร้อมกับบทความต้นฉบับที่ได้แก้ไขครั้งสุดท้าย นอกจากนี้ ผู้นิพนธ์ทุกท่านต้องยืนยันว่าบทความ ต้นฉบับที่ส่งมาตีพิมพ์นั้น ได้ส่งมาตีพิมพ์เฉพาะในวารสาร วิชาการธรรม ทรรศน์ เพียงแห่งเดียวเท่านั้น หากมีการใช้ ภาพหรือตารางของผู้นิพนธ์อื่นที่ปรากฏในสิ่งตีพิมพ์อื่นมาแล้ว ผู้นิพนธ์ต้องขออนุญาตเจ้าของลิขสิทธิ์ก่อน พร้อมทั้ง แสดงหนังสือที่ได้รับการยินยอมต่อบรรณาธิการ ก่อนที่บทความจะได้รับการตีพิมพ์References
ทิศนา แสงระวี และเรชา ชูสุวรรณ. (2565). ครูไทยกับการจัดการเรียนรู้ในยุค Digital Disruption. วารสารมหาจุฬานาครทรรศน์, 9(4), 13-26.
นิชานันท์ วรรณกุล. (2564). อิทธิพลของแรงจูงใจในการปฏิบัติงานที่ส่งผลต่อประสิทธิผลการปฏิบัติงานของข้าราชการส่วนท้องถิ่นในเขตจังหวัดสกลนคร. (วิทยานิพนธ์รัฐประศาสนศาสตรมหาบัณฑิต). สกลนคร: มหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏสกลนคร.
พิไลวรรณ มาแป. (2560). ปัญหาและแนวทางการพัฒนาการใช้เทคโนโลยีสารสนเทศในการจัดการศึกษาของครูในโรงเรียน อำเภอสอยดาว สังกัดสำนักงานเขตพื้นที่การศึกษาประถมศึกษาจันทบุรี เขต 2. (วิทยานิพนธ์การศึกษามหาบัณฑิต). ชลบุรี: มหาวิทยาลัยบูรพา.
ภัทรนันท์ ไวทยะสิน. (2562). “เปลี่ยน” ผู้เรียนเป็นนวัตกร นวัตกรรมใหม่ของการเรียนการสอนในยุคการศึกษา 4.0. วารสารเทคโนโลยีและสื่อสารการศึกษา, 14(17), 37-51.
มณีรัตน์ ชัยยะ. (2566). การบริหารทรัพยากรมนุษย์ภายใต้การเปลี่ยนแปลงสู่ยุคดิจิทัล (Digital HR). Journal of Administrative and Management Innovation, 11(1), 104-115.
สำนักงานเขตพื้นที่การศึกษามัธยมศึกษากรุงเทพมหานคร เขต 2. (2566). แผนปฏิบัติราชการประจำปีงบประมาณ พ.ศ. 2566. กรุงเทพฯ: สำนักงานเขตพื้นที่การศึกษามัธยมศึกษากรุงเทพมหานคร เขต 2.
สุดคนึง ปกปิด. (2561). ปัจจัยเชิงสาเหตุที่ส่งผลต่อประสิทธิภาพและประสิทธิผลการปฏิบัติงานของข้าราชการครู สังกัดสำนักงานเขตพื้นที่การศึกษาประถมศึกษาลำปาง เขต 1 เขต 2 และเขต 3. วารสารมหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏลำปาง, 8(1), 139-157.
สุนันท์ สีพาย. (2562). บทบาทของครูไทยในการศึกษา 4.0. วารสารการวัดผลการศึกษา, 25(2), 3-14.
สุปรียา ไตรยะขันธ์. (2565). สภาพปัญหาและแนวทางพัฒนาการจัดการเรียนรู้ของครูในยุคดิจิทัล สังกัดสำนักงานเขตพื้นที่การศึกษาประถมศึกษานครพนม เขต 1. วารสาร มจร อุบลปริทรรศน์, 7(3), 931-944.
สุภารัตน์ กุลโชติ. (2566). แรงจูงใจที่ส่งผลต่อประสิทธิผลในการปฏิบัติงานของบุคลากร สังกัดเทศบาลนครหาดใหญ่ จังหวัดสงขลา. (วิทยานิพนธ์รัฐประศาสนศาสตรมหาบัณฑิต). สงขลา: มหาวิทยาลัยสงขลานครินทร์.
สุวรรณา สุ่มเนียม. (2559). การพัฒนาโมเดลเชิงสาเหตุของปัจจัยที่ส่งผลต่อประสิทธิผลการทำงานของครูอาชีวศึกษา. วารสารมหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏธนบุรี, 10(2), 48-61.
อัครัช แสนสิงห์. (2560). บรรยากาศองค์กรที่มีผลต่อแรงจูงใจใฝ่สัมฤทธิ์ในการทำงานของพนักงานประจำสำนักงาน บริษัท เดอะมอลล์กรุ๊ป จำกัด สาขานครราชสีมา. (การค้นคว้าอิสระบริหารธุรกิจมหาบัณฑิต). นครราชสีมา: มหาวิทยาลัยเทคโนโลยีราชมงคลอีสาน.
Ally, M. (2019). Competency Profile of the Digital and Online Teacher in Future Education. International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning, 20(2), 302-318.
Fanreza R. (2018). The Quality of Teachers in Digital Era. 5th International Conference on Community Development (AMCA 2018), July 2018, (pages 461-463). Atlantis Press.
Halpin, A. W., & Croft, D. B. (1963). The Organizational Climate of School. Midwest: The University of Chicago.
Krejcie, R. V., & Morgan, D. W. (1970). Determining Sample Size for Research Activities. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 30(3), 607-610.
Litwin, G. H., & Stringer Jr., R. A. (1968). Motivation and Organizational Climate. Oxford: England Harvard University.
Okeke, J. N. J., et al. (2020). School Climate As Predictor Of Teachers Job Performance In Secondary Schools In Anambra State, Nigeria. International Journal of Education and Research, 8(3), 17-26.
Sergiovanni, T. J., & Starratt, R. J. (1979). Supervision: Human Perspectives. New York: McGraw Hill.
UNESCO. (2021). Digital transformation in education in Asia Pacific. Paper presented at the 2nd ASIA-PACIFIC REGIONAL EDUCATION MINISTER'S CONFERENCE (APREMC-II). Retrieved from https://knowledgehub.sdg4education2030.org/system/files/2022 06/Digital%20Transformation-min.pdf
Widyaningsih, H., Darmawan, R. & Pelana, R. (2021). Influence of organizational climate and teaching motivation on the performance of physical education teachers. Journal of Physical Education and Sport, 21(4), 2408-2412.
Yentri, A. (2020). Language Teaching in the Digital Age: Teachers` Views and Its Challenges. Research and Innovation in Language Learning, 3(3), 163-172.