High-Performance School Administration Model based on Sappurisdhamma of the Administrators of Schools Affiliated with Pattaya City, Chonburi Province
Main Article Content
Abstract
The purposes of this research were: 1) to study the management conditions of high-performance school administration in schools affiliated with Pattaya City, Chonburi Province; 2) to develop a high-performance school administration model based on Sappurisdhamma for the administration of schools affiliated with Pattaya City, Chonburi Province; and 3) to evaluate the model. Mixed methods research was used with three steps1: Study the management conditions using questionnaires with 260 educators, administrators, teaching staff, and the Basic Education Commission of schools under Pattaya City, Chonburi Province. Data were analyzed using statistics, mean, and standard deviation. Step 2: Develop the model by interviewing 10 key informants using a semi-structured interview form, and conducting a group discussion with 10 experts using question guidelines in the group discussion. Key informants and experts were selected through specific methods. Data were analyzed using content analysis. Step 3: Evaluate the model using the evaluation form with 260 administrators, teachers, and members of the Basic Education Commission of schools under Pattaya City, Chonburi Province. Data were analyzed using statistics, mean, and standard deviation.
The results revealed that:
1. The results revealed that the conditions of high-performance school administration in schools affiliated with Pattaya City, Chonburi Province were at a high level (x̄ = 4.26). This included the aspect of corporate culture (x̄ = 4.29), the aspect of network organization (x̄ = 4.28), the aspect of strategy management (x̄ = 4.28), the aspect of good governance (x̄ = 4.24), and the aspect of information technology (x̄ = 4.22), respectively.
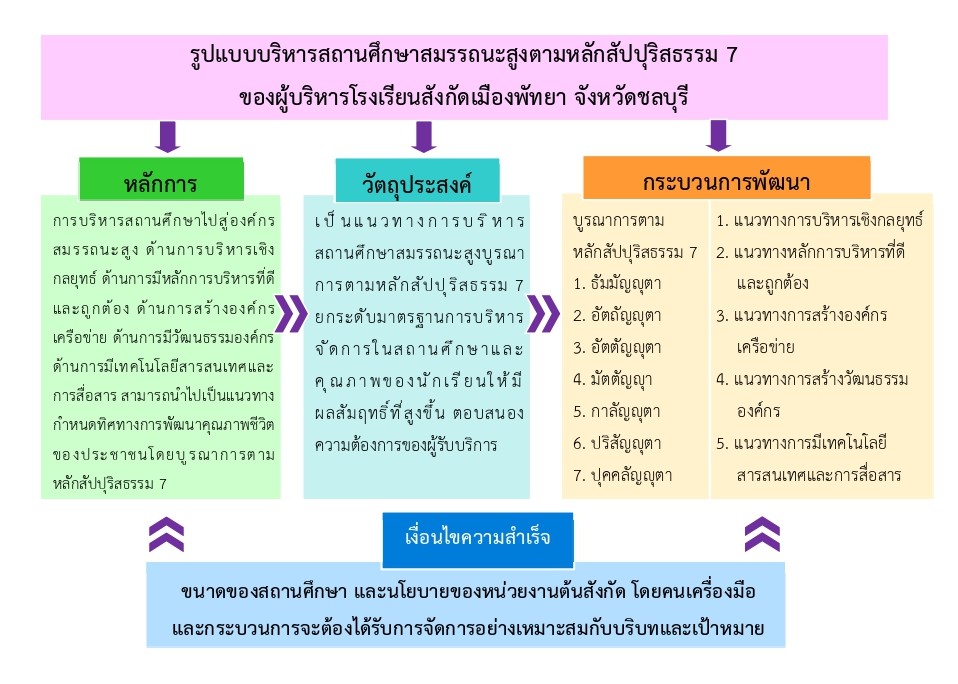
2. A high-performance school administration model based on Sappurisdhamma for the administrators of schools affiliated with Pattaya City, Chonburi Province was developed, which included: 1) principles, 2) objectives, 3) development processes, and 4) conditions for success.
3. Evaluate the model all over at a high level included useful (x̄ = 4.47), correct (x̄ = 4.43), appropriate (x̄ = 4.42), and possible (x̄ = 4.38) respectively.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
เพื่อให้เป็นไปตามกฎหมายลิขสิทธิ์ ผู้นิพนธ์ทุกท่านต้องลงลายมือชื่อในแบบฟอร์มใบมอบลิขสิทธิ์บทความ ให้แก่วารสารฯ พร้อมกับบทความต้นฉบับที่ได้แก้ไขครั้งสุดท้าย นอกจากนี้ ผู้นิพนธ์ทุกท่านต้องยืนยันว่าบทความ ต้นฉบับที่ส่งมาตีพิมพ์นั้น ได้ส่งมาตีพิมพ์เฉพาะในวารสาร วิชาการธรรม ทรรศน์ เพียงแห่งเดียวเท่านั้น หากมีการใช้ ภาพหรือตารางของผู้นิพนธ์อื่นที่ปรากฏในสิ่งตีพิมพ์อื่นมาแล้ว ผู้นิพนธ์ต้องขออนุญาตเจ้าของลิขสิทธิ์ก่อน พร้อมทั้ง แสดงหนังสือที่ได้รับการยินยอมต่อบรรณาธิการ ก่อนที่บทความจะได้รับการตีพิมพ์References
กระทรวงศึกษาธิการ. (2552). หลักสูตรแกนกลางการศึกษาขั้นพื้นฐาน พุทธศักราช 2551 สำนักงานคณะกรรมการการศึกษาขั้นพื้นฐาน. กรุงเทพฯ: ชุมนุมสหกรณ์การเกษตรแห่งประเทศไทย.
นันทวรรณ อิสรานุวัฒน์ชัย. (2550). ภาวะผู้นำที่พึงประสงค์ในยุคโลกาภิวัตน์: ศึกษาจากหลักพุทธธรรม. (วิทยานิพนธ์พุทธศาสตรมหาบัณฑิต). พระนครศรีอยุธยา. มหาวิทยาลัยมหาจุฬาลงกรณราชวิทยาลัย.
พระเปลี่ยน ปญฺญาปทีโป. (2552). สัปปุริสธรรม 7 อย่าง. กรุงเทพฯ: สุภา.
พระธรรมปิฎก (ป.อ. ปยุตโต). (2546). สู่การศึกษาแนวพุทธ. (พิมพ์ครั้งที่ 2). กรุงเทพฯ: กระทรวงศึกษาธิการ.
พิเชษฐ์ โพธิ์ภักดี. (2553). การพัฒนารูปแบบการบริหารโรงเรียนนิติบุคคล สำนักงานคณะกรรมการการศึกษาขั้นพื้นฐาน. (วิทยานิพนธ์ครุศาสตรดุษฎีบัณฑิต). กรุงเทพฯ: จุฬาลงกรณ์มหาวิทยาลัย.
สำนักการศึกษาเมืองพัทยา. (2563). บทสรุปสำหรับผู้บริหาร ผลการทดสอบทางการศึกษาระดับชาติขั้นพื้นฐาน (O-NET) ปีการศึกษา 2562. (เอกสารประกอบการประชุม). ชลบุรี: เมืองพัทยา.
สำนักงานเลขาธิการสภาผู้แทนราษฎร. (2562). ความมุ่งหมายและคำอธิบายประกอบรายมาตราของรัฐธรรมนูญแห่งราชอาณาจักรไทย พุทธศักราช 2560. กรุงเทพฯ: สำนักงานเลขาธิการสภาผู้แทนราษฎร.
สำนักงานคณะกรรมการพัฒนาระบบราชการ. (2556). แผนยุทธศาสตร์การพัฒนาระบบราชการไทย (พ.ศ. 2556-พ.ศ. 2561). กรุงเทพฯ: สำนักงานคณะกรรมการพัฒนาระบบราชการ (ก.พ.ร.).
สุธีรัตน์ อริเดช และพูนชัย ยาวิราช. (2557). ยุทธสาสตร์การพัฒนาวัฒนธรรมคุณภาพของสถานศึกษาขั้นพื้นฐานของรัฐ. วารสารราชพฤกษ์, 12(2), 31-37.
Holbeche, L. (2005). The high-performance organization: Creating dynamic stability and sustainable success. Oxford, UK: Elsevier/Butterworth-Heinemann.
Krejcie, R. V., & Morgan, D. W. (1970). Determining Sample Size for Research Activities. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 30, 607-610. https://doi.org/10.1177/001316447003000308.
McMillan, J. H., & Schumacher, S. (2001). Research in Education. (5th ed.). New York: Addison Wesley Longman, Inc.
Mille, L. M. (2009). The High-performance Organization an Assessment of Virtues and Values PreparedforEuropean. Retrieved from http//www. opdc.go.th./oldweb/thai/High-performance/HPO
Schemerhorn, J. R., Hunt, J. G., & Osborn, R. N. (2003). Organizational behavior. (8th ed.). USA: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.