การวิเคราะห์องค์ประกอบเชิงยืนยันอันดับสองของโมเดลการวัดความท้าทายในการนำปัญญาประดิษฐ์มาใช้ในงานบริหารทรัพยากรมนุษย์ของอุตสาหกรรมไมซ์
คำสำคัญ:
ปัญญาประดิษฐ์, งานบริหารทรัพยากรมนุษย์, อุตสาหกรรมไมซ์, การวิเคราะห์องค์ประกอบเชิงยืนยันอันดับสองบทคัดย่อ
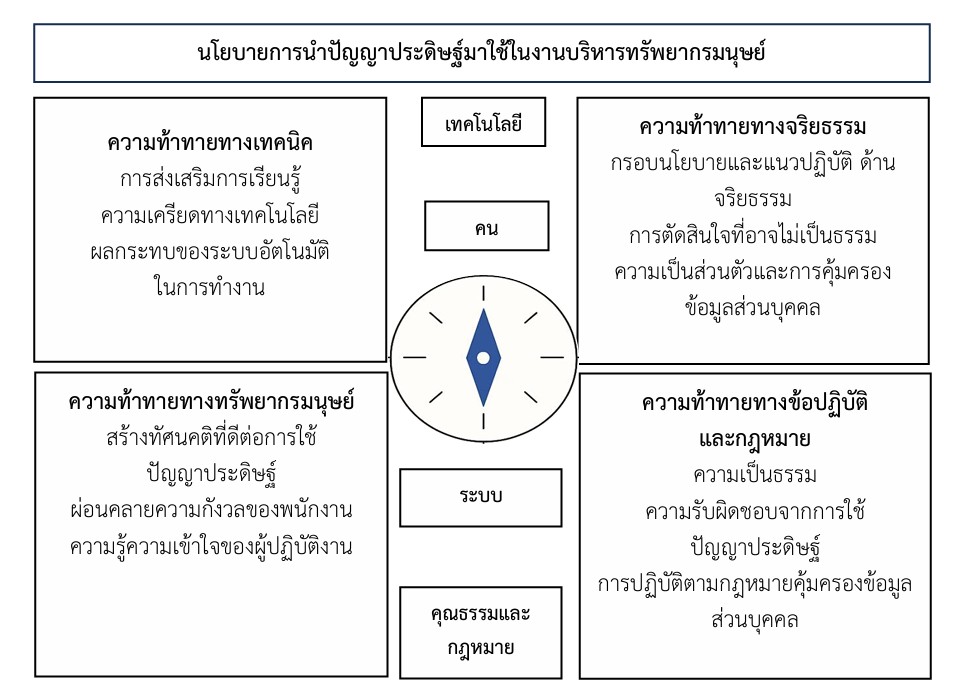
การวิจัยนี้มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อ (1) วิเคราะห์องค์ประกอบเชิงยืนยันอันดับสองของโมเดลการวัดความท้าทายในการนำปัญญาประดิษฐ์มาใช้ในงานบริหารทรัพยากรมนุษย์ของอุตสาหกรรมไมซ์ และ (2) ทดสอบความสอดคล้องของโมเดลการวัดความท้าทายในการนำปัญญาประดิษฐ์มาใช้ในงานบริหารทรัพยากรมนุษย์ของอุตสาหกรรมไมซ์ ตัวอย่างที่ใช้ในการวิจัย ได้แก่ พนักงานตั้งแต่ระดับปฏิบัติการไปจนถึงผู้บริหารระดับสูงในฝ่ายทรัพยากรมนุษย์ของบริษัทในกลุ่มธุรกิจอุตสาหกรรมไมซ์ (MICE) ในเขตกรุงเทพมหานคร และปริมณฑล จำนวน 400 คน ได้มาโดยการสุ่มแบบเจาะจง เครื่องมือที่ใช้ในการวิจัย คือ แบบสอบถาม สถิติที่ใช้ในการวิเคราะห์ข้อมูลได้แก่ ความถี่ ร้อยละ ทดสอบไคเซอร์-เมเยอร์-โอลกิน และวิเคราะห์องค์ประกอบเชิงยืนยันอันดับสอง ผลการวิจัยพบว่า 1) โมเดลการวัดความท้าทายในการนำปัญญาประดิษฐ์มาใช้ในงานบริหารทรัพยากรมนุษย์ของอุตสาหกรรมไมซ์ ประกอบไปด้วย 4 องค์ประกอบ ได้แก่ ความท้าทายทางเทคนิค (TEC) ความท้าทายทางจริยธรรม (ETH) ความท้าทายทางทรัพยากรมนุษย์ (HRM) และ ความท้าทายทางข้อปฏิบัติและกฎหมาย (LAW) โดยมีค่าน้ำหนักองค์ประกอบย่อยของแบบวัดทั้ง 4 องค์ประกอบเป็นไปตามเกณฑ์ และ 2) การทดสอบความสอดคล้องของโมเดลการวัดความท้าทายในการนำปัญญาประดิษฐ์มาใช้ในงานบริหารทรัพยากรมนุษย์ของอุตสาหกรรมไมซ์ พบว่า มีค่าไค-สแควร์ เท่ากับ 293.941 ที่ชั้นแห่งความอิสระ df เท่ากับ 126 ค่า CMIN/df เท่ากับ 2.333 ค่าประมาณความคลาดเคลื่อนของรากกำลังสองเฉลี่ย RMSEA เท่ากับ 0.058 ค่าเฉลี่ยของความคลาดเคลื่อน RMR เท่ากับ 0.024 ค่าดัชนีวัดความสอดคล้อง GFI เท่ากับ 0.935 ค่าดัชนีวัดความสอดคล้อง CFI เท่ากับ 0.979 ค่าดัชนีวัดเปอร์เซ็นต์ความกลมกลืน NFI เท่ากับ 0.965 แสดงว่าโมเดลการวัดความท้าทายในการนำปัญญาประดิษฐ์มาใช้ในงานบริหารทรัพยากรมนุษย์ของอุตสาหกรรมไมซ์ มีความสอดคล้องของโมเดลกับข้อมูลเชิงประจักษ์
เอกสารอ้างอิง
ชลลดา มงคลวนิช และ รัตนาภรณ์ ชาติวงศ์. (2560). แนวทางการพัฒนาบุคลากรที่ขาดแคลนในอุตสาหกรรมไมซ์ กรณีศึกษา : สถานที่จัดงานประเภทโรงแรม. วารสารการบริการและการท่องเที่ยวไทย, 12(1), 50-65.
นิธิกิตติกานต์ เหมสุวรรณ, เกิดศิริ เจริญวิศาล และ สันติธร ภูริภักดี. (2567). ศักยภาพและความพร้อม: การเป็นจุดหมายปลายทางสำหรับอุตสาหกรรมไมซ์ของ ประเทศไทย. วารสารการบริการและการท่องเที่ยวไทย, 19(2), 54-66.
พัฒน์ศิณีนาฎ วรรณรัตน์. (2567). การศึกษานวัตกรรมปัญญาประดิษฐ์เพื่อการบริหารทรัพยากรมนุษย์กรณีศึกษา ของบริษัทในกลุ่มธุรกิจอุตสาหกรรมไมซ์ (MICE). (การจัดการมหาบัณฑิต, มหาวิทยาลัยมหิดล).
Abdeldayem, M. M., & Aldulaimi, S. H. (2020). Trends and opportunities of artificial intelligence in human resource management: Aspirations for public sector in Bahrain. International journal of scientific and technology research, 9(1), 3867-3871.
Adeyelu, O. O., Ugochukwu, C. E., & Shonibare, M. A. (2024). The impact of artificial intelligence on accounting practices: Advancements, challenges, and opportunities. International Journal of Management & Entrepreneurship Research, 6(4), 1200-1210.
Barney, J. (1991). Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. Journal of management, 17(1), 99-120.
Brown, T. A. (2015). Confirmatory Factor Analysis for Applied Research. (2nd ed.). New York: Guilford Press.
Diamantopoulos, A., Sarstedt, M., Fuchs, C., Wilczynski, P., & Kaiser, S. (2012). Guidelines for choosing between multi-item and single-item scales for construct measurement: a predictive validity perspective. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 40(3), 434-449.
Ekuma, K. (2024). Artificial intelligence and automation in human resource development: A systematic review. Human Resource Development Review, 23(2), 199-229.
Field, A. (2018). Discovering Statistics Using IBM SPSS Statistics. (5th ed.). California: Sage Publications.
Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., Anderson, R. E., & Tatham, R. L. (2019). Multivariate Data Analysis. (8th ed.). Hampshire: Cengage Learning, EMEA.
Hu, L. T., & Bentler, P. M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural equation modeling: a multidisciplinary journal, 6(1), 1-55.
Kaur, M., & Gandolfi, F. (2023). Artificial intelligence in human resource management-challenges and future research recommendations. Revista de Management Comparat International, 24(3), 382-393.
Khan, F. A., Khan, N. A., & Aslam, A. (2024). Adoption of artificial intelligence in human resource management: an application of TOE-TAM model. Research and review: human resource and labour management, 5(1), 22-36.
Kline, R. B. (2023). Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling. New York: Guilford Publications.
Lutfi, L., & Mohammadi, A. (2025). Opportunity of Implementation Artificial Intelligence in Human Resources Management. International Journal of Academic Reserach in Economics and Management Sciences, 14(1), 212-228.
Matos, F., Vairinhos, V., Salavisa, I., Edvinsson, L., & Massaro, M. (2020). Knowledge, people, and digital transformation. Cham: Springer.
Mice Intelligence Center. (2019). ปัญญาประดิษฐ์ (AI) คือ กุญแจสู่อนาคตสำหรับธุรกิจไมซ์. สืบค้นจาก https://intelligence.businesseventsthailand.com/files/insights/57315573724821.pdf.
Mintz, Y., & Brodie, R. (2019). Introduction to artificial intelligence in medicine. Minimally Invasive Therapy & Allied Technologies, 28(2), 73-81.
Nawaz, N., Arunachalam, H., Pathi, B. K., & Gajenderan, V. (2024). The adoption of artificial intelligence in human resources management practices. International Journal of Information Management Data Insights, 4(1), 100208.
Niehueser, W., & Boak, G. (2020). Introducing artificial intelligence into a human resources function. Industrial and commercial training, 52(2), 121-130.
Nimmagadda, B., Vangaveti, Y., Aaluri, S., & Rao, C. M. (2024). An Analytical study on Navigating Sustainability Challenges and Opportunities in the era of AI and the Gig Economy. Retrieved from https://www.matec-conferences.org/articles/matecconf/pdf/2024/04/matecconf_icmed2024_01044.pdf
Paigude, S., Pangarkar, S. C., Hundekari, S., Mali, M., Wanjale, K., & Dongre, Y. (2023). Potential of artificial intelligence in boosting employee retention in the human resource industry. International Journal on Recent and Innovation Trends in Computing and Communication, 11(3s), 01-10.
Palos-Sánchez, P. R., Baena-Luna, P., Badicu, A., & Infante-Moro, J. C. (2022). Artificial intelligence and human resources management: A bibliometric analysis. Applied Artificial Intelligence, 36(1), 2145631.
Qiu, L., & Zhao, L. (2018). Opportunities and challenges of artificial intelligence to human resource management. Academic Journal of Humanities & Social Sciences, 2(1), 144-153.
Sanyaolu, E., & Atsaboghena, R. (2022). Role of Artificial Intelligence in Human Resource Management: Overview of its benefits and challenges. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Eniola-Sanyaolu/publication/366307222_Role_of_Artificial_Intelligence_in_Human_Resource_Management_Overview_of_its_benefits_and_challenges/links/639b490fe42faa7e75c5888c/Role-of-Artificial-Intelligence-in-Human-Resource-Management-Overview-of-its-benefits-and-challenges.pdf.
Schumacker, E., & Lomax, G. (2016). A beginner’s guide to structural equation modelling. (4th ed). London: Routledge.
Shahzad, M. F., Xu, S., Naveed, W., Nusrat, S., & Zahid, I. (2023). Investigating the impact of artificial intelligence on human resource functions in the health sector of China: A mediated moderation model. Heliyon, 9(11), 1-17.
Sirivadhanawaravachara, A. (2025). The role and impact of MICE (Meetings, Incentives, Conferences, and Exhibitions) industry in Thailand. World Journal of Advanced Research and Reviews, 25(1), 708-719.
Tewari, I., & Pant, M. (2020). Artificial intelligence reshaping human resource management: A review. In 2020 IEEE international conference on advent trends in multidisciplinary research and innovation (ICATMRI) (pp. 1-4). New York: IEEE.
Venkatesh, V., & Davis, F. D. (2000). A theoretical extension of the technology acceptance model: Four longitudinal field studies. Management science, 46(2), 186-204.
Vishwakarma, L. P., & Singh, R. K. (2023). An analysis of the challenges to human resource in implementing artificial intelligence. In The adoption and effect of artificial intelligence on human resources management, Part B (pp. 81-109). Leeds: Emerald Publishing Limited.
Vrontis, D., Christofi, M., Pereira, V., Tarba, S., Makrides, A., & Trichina, E. (2021). Artificial intelligence, robotics, advanced technologies and human resource management: a systematic review. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 33(6), 1237–1266.
Yanamala, K. K. R. (2023). Transparency, privacy, and accountability in AI-enhanced HR processes. Journal of Advanced Computing Systems, 3(3), 10-18.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2025 วารสารสังคมศาสตร์ปัญญาพัฒน์

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.

