A Study of Basic Science Process Skills and Social Behavior of Early Childhood Students from Inquiry Method
Keywords:
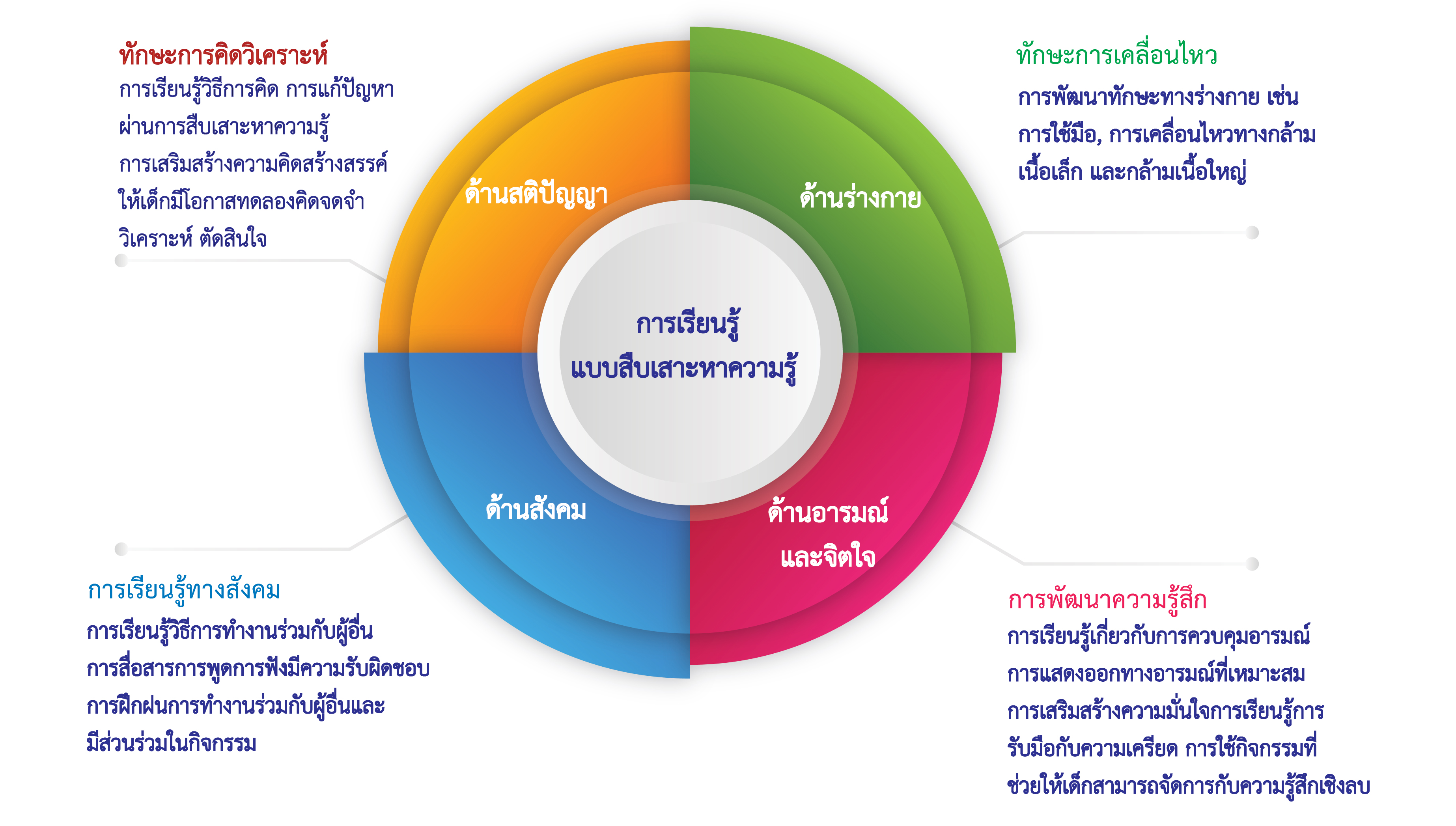
Basic Scientific Process Skills, Inquiry-Based Learning, Social BehaviorAbstract
This research aims to: 1) study basic scientific process skills, 2) compare basic scientific process skills, 3) examine the social behavior of early childhood children through inquiry-based learning experiences, and 4) compare social behavior before and after implementing inquiry-based learning experiences. The study is a quasi-experimental research. The sample group consisted of 30 kindergarten level 3/4 students from Kanchanaburi Kindergarten School, Mueang District, Kanchanaburi Province, during the first semester of the 2014 academic year. The research instruments included 21 inquiry-based learning experience plans. Data collection tools consisted of a test measuring basic scientific process skills and an observation form for social behavior. Statistical methods used for data analysis were mean, standard deviation, percentage, and t-test.
The research findings are as follows:
1. Early childhood children demonstrated improved basic scientific process skills after participating in inquiry-based learning experiences, with an average score of 24.22, a standard deviation of 1.74, and a percentage of 96.88. Prior to the experiences, the average score was 18.57, with a standard deviation of 2.73 and a percentage of 74.28. The progress score had an average of 5.65, representing 22.6%.
2. Early childhood children exhibited improved social behavior after participating in inquiry-based learning experiences, with an average score of 22.68, a standard deviation of 2.03, and a percentage of 94.52. Before the experiences, the average score was 17.06, with a standard deviation of 3.98 and a percentage of 71.09. The progress score had an average of 5.62, representing 23.43%.
3. The basic scientific process skills of early childhood children after participating in inquiry-based learning experiences were significantly higher than before, at a statistical significance level of .05.
4. The social behavior of early childhood children after participating in inquiry-based learning experiences was significantly higher than before, at a statistical significance level of .05.
References
กระทรวงศึกษาธิการ. (2560). หลักสูตรการศึกษาปฐมวัยพุทธศักราช 2560. กรุงเทพฯ: ชุมนุมสหกรณ์การเกษตรแห่งประเทศไทย จำกัด.
ชัยวัฒน์ สุทธิรัตน์. (2561). 80 นวัตกรรมการจัดการเรียนรู้ที่เน้นผู้เรียนเป็นสำคัญ. นนทบุรี: พีบาลานซ์ดีไซด์ แอนปริ้นติ้ง.
เยาวนุช ทานาม. (2557). การพัฒนารูปแบบการจัดการเรียนรู้ PLAY เพื่อพัฒนาทักษะทางสังคมของเด็กปฐมวัย. (ปริญญานิพนธ์การศึกษาดุษฎีบัณฑิต). กรุงเทพฯ: มหาวิทยาลัยศรีนครินทรวิโรฒ.
รัศมี อ่วมน้อย. (2558). การพัฒนากิจกรรมการจัดประสบการณ์การเรียนรู้แบบสืบเสาะหาความรู้โดยใช้สมองเป็นฐานที่มีต่อทักษะกระบวนการทางวิทยาศาสตร์ของเด็กปฐมวัยชั้นอนุบาลปีที่ 1 โรงเรียนบ้านวังหันน้ำดึง อำเภอคลองลุง จังหวัดกำแพงเพชร. วารสารวิชาการเครือข่ายบัณฑิตศึกษามหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏภาคเหนือ, 5, 37-52.
วรรณทิพา รอดแรงค้า. (2540). ทักษะและกระบวนการในวิทยาศาสตร์ศึกษา. กรุงเทพฯ: สถาบันพัฒนาวิชาการ ภาควิชาการศึกษา คณะศึกษาศาสตร์มหาวิทยาลัยเกษตรศาสตร์.
สมบูรณ์ ตันยะ. (2550). การประเมินทางการศึกษา. กรุงเทพฯ: สุวีริยาสาส์น.
สิริมา ภิญโญอนันต์พงษ์. (2545). การวัดและประเมินผลแนวใหม่: เด็กปฐมวัย. กรุงเทพฯ: ภาควิชา หลักสูตรและการสอน คณะศึกษาศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยศรีนครินทรวิโรฒ.
Lawson, H. (2001). Active Citizenship in Schools and the Community. Curriculum Journal, 12, 163-178.
Piaget, J. (1970). The origins of intelligence in children. New York: Norton.